Fraud Week 2020: Got Situational Awareness?

Looking at the Fraud Triangle During COVID-19
Today, we continue our special 5-part Fraud Week Coffee Break Series with another episode to address important fraud prevention topics with insight from our Certified Fraud Examiners and subject matter experts. Fraud Week is an annual movement, organized by the Association for Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), to champion the need to proactively fight fraud and help safeguard businesses and investments from the growing fraud problem.
For this episode, we interviewed Carlos Rivera, CFE, MAFF, Senior Vice President – Caribbean & Latin America of Lowers Forensics International and Grant Mizel, Financial Analyst, Emerging Markets for Lowers Risk Group. Rivera and Mizel offer their insight to help us understand the importance of situational awareness to an organization’s ability to detect and prevent fraud. They point to the Fraud Triangle as a model for understanding why fraud happens, but also recognize that without situational awareness, the Fraud Triangle is meaningless.
Grab a cup of coffee and spend 7 minutes with Rivera and Mizel:
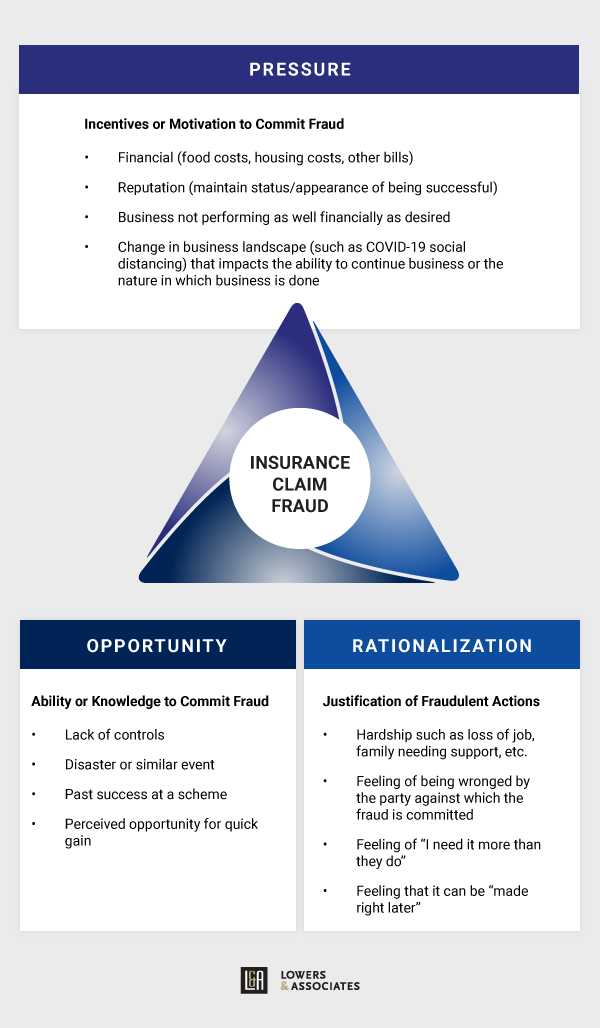
Formulated in 1953 by criminologist Donald Cressey, the Fraud Triangle theorizes that fraud occurs when a perpetrator feels financial pressure, they are presented an opportunity, and/or they can rationalize the theft. For the Fraud Triangle to be valuable, organizations must be situationally aware. What’s going on in, around, and outside your organization? Which of these internal or external factors might be impacting the opportunities, rationalizations, and incentives that can lead people to commit fraud?
As Rivera points out, “Removing separation of duties and internal audit departments certainly creates the opportunity for employees to commit fraud. However, you have to consider the financial pressure and rationalization that goes along with a national catastrophic situation. In many instances, you’ll have employees who receive salary cuts that may not only feel financial pressure but also rationalize it by claiming what they believe is rightfully theirs, or you may see an employee rationalize through necessity which I believe can be just as powerful of a motivator.”
The COVID-19 pandemic has, unfortunately, led to situations where people have less supervision, more opportunity, and way more financial pressure than before.
As a result, in its September 2020 Fraud in the Wake of COVID-19 Benchmarking Report, the ACFE reported, “77% of respondents said they had observed an increase in the overall level of fraud, with one-third noting that this increase has been significant.” Furthermore, the ACFE reports, “Our findings indicate this uptick is likely to continue; 92% of respondents expect to see a further increase in the overall level of fraud during the next year, and nearly half expect that increase to be significant.”
Mizel remarks, “You talk about the Fraud Triangle and opportunity, when you give folks the opportunity, they are most likely going to take advantage. You can head that off by putting structures in place, rigor, documentation, automated processes… when you think about the employee, it’s not strange from a fraud examiner’s perspective that someone without oversight would take advantage of the situation.”
We hope you enjoyed this Coffee Break episode. Come back tomorrow to hear from Steven Schwartz, Chief Revenue Officer of Periculus, about cyberfraud during COVID-19.